What is CTA?
Coronary CT angiography is a quick, non-invasive test that uses computed tomography (CT) to look at blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (the “coronary arteries”). Coronary CT angiography (CTA) allows your physician to see whether or not plaque has developed in the coronary arteries that may result in “blockages” that might cause symptoms or increase your risk of a future heart attack.
Benefits of CTA
CTA is especially useful to decide that the coronary arteries are not the cause of chest discomfort or shortness of breath. Also, CTA is able to find both severe blockages, as well as any plaque buildup in the coronary arteries that may not be causing severe narrowing at present but may lead to heart problems in the future.
When is CTA used?
CTA is generally considered best for individuals with symptoms but who have no prior history of coronary artery disease or who have unclear findings from a stress test. In certain cases, CTA may be considered appropriate for patients who have previously experienced heart attacks, or who have undergone coronary stent placement or coronary artery bypass surgery. Numerous other possible indications exist for CTA, which may be further explained by your doctor.
How is CTA performed?
CT is a non-invasive technique that uses x-rays to obtain images of the body. An electrocardiogram, or measure of a patient’s heart rhythm, is recorded during the CTA examination so that images can be matched with the motion of the heart. During the CTA, contrast (iodine dye) is injected in your vein so that the coronary arteries can be seen. Some patients may feel a “warm” sensation when the contrast is injected. Allergic reactions to the contrast dye occur very rarely.
How to prepare for CTA
Based upon your condition and the doctor performing the CTA, you may be asked to do the following–always check with your doctor for your preparation before the test:
* Take a beta-blocker medication to lower your heart rate. Some centers may give such medications by mouth and/or inject it through a vein prior to the test. This will help create the best images of the moving heart.
* Avoid caffeinated drinks or food (e.g. coffee, tea, sodas, energy drinks, chocolate) for 12 – 24 hours prior to your test.
* Do not eat for 4 hours or drink anything for 1 hour before the test (this may vary, please be sure to check with your doctor’s office prior to your test).
* Do not take certain medications such as Viagra, Cialis, or Levitra for at least 48 – 78 hours prior to your test.
* Temporarily stop taking Glucophage (Metformin) for 48 hours after the test.
* Inform your doctor of any medications you are taking – including over-the-counter pain medications such as Advil or Motrin.
* Inform your doctor and the CT technologist if you have any allergies to contrast material. If you have had prior reaction to injected contrast, your doctor may prescribe medications to reduce the risk of such a reaction.
* A women should inform her doctor and the CT technologist if there is any possibility that she is pregnant.
* If needed, blood tests will be drawn to check for kidney disease prior to the test. Individuals with mild kidney disease can still receive injected contrast but may require additional medications and IV fluids before or after the test.
* If you have irregular heartbeats it may make it difficult to get good CT images, and this should be clearly mentioned when your appointment is made.
What will happen during the CTA?
A nurse or technologist may ask you to remove your clothes above the waist and wear a hospital gown. You may be asked to remove metal objects such as jewelry, which can affect the CT images.
* An intravenous (IV) line will be inserted into a vein in your arm.
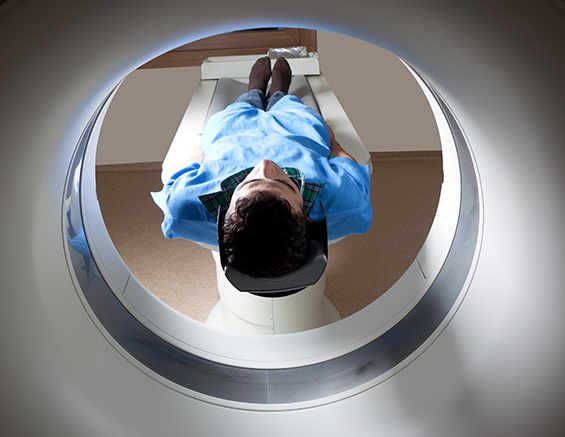
* The CT scanner is a machine with a large ring-like or doughnut-like structure that has a sliding bed in its center. You will be asked to lie on your back on the scanner bed. While you may lie on this table for approximately 10 – 30 minutes, most of this time will involve preparation. The actual images only take a few seconds to obtain.
* The technologist or nurse will apply sticky patches called electrodes on your chest. This will be used to monitor your heartbeat during the exam.
* You will be asked to lie still and you will receive instructions to hold your breath for short periods of time (less than 15 seconds) while pictures are taken. It is very important to be absolutely still and not breathe, move, or swallow while the pictures are being taken.
* During some steps of the test, contrast dye will be injected through the IV. This may cause a warm feeling all over your body, which usually disappears within a minute or so.
Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) Scan
In some cases, your doctor may order a Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) scan. This study may often be ordered for patients who do not experience any symptoms but may provide your doctor with more information regarding plaque build-up in your heart arteries. While there are many similarities between a CAC scan and a CTA, the CAC scan does not require an injection of contrast dye or the use of an IV line in your vein.
CAC scans can be used to show hardened plaque build-up in the coronary arteries, which allows your doctor to estimate the risk of future heart attacks. However, a CAC scan cannot show blockages in the coronary arteries.
